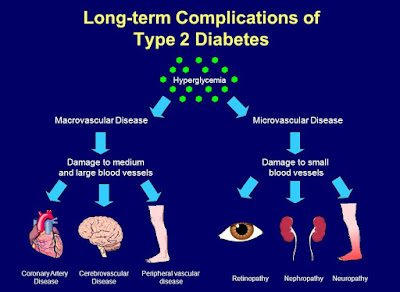
High blood glucose levels can damage blood vessels, nerves and organs. Below are complications of the raised blood glucose in type 2 diabetes;
• Heart and Artery Troubles
If you don't treat diabetes with a healthy diet and exercise, you're more likely to get plaque in your arteries than people who don't have it. This sticky substance slows blood flow and increases your risk of clots. It leads to hardening of the arteries (called atherosclerosis), which makes you more likely to have a heart attack or stroke. About 2 of 3 people with diabetes die of heart disease.
• Kidney Complications
• Eye Problems
• Diabetic Neuropathy and Nerve Pain
Over time, uncontrolled diabetes and high blood sugar can cause nerve damage. Symptoms include tingling, numbness, pain, and a pins and needles sensation - often in your fingers, hands, toes, or feet. The damage can't be reversed, but there are treatments. Controlling your diabetes can help prevent further harm.
• Foot Injuries Can Take a Toll
• Teeth and Gums Are Targets
High blood sugar levels can feed the bacteria that make plaque. Plaque buildup leads to cavities, tooth decay, and gum disease. Severe gum disease can cause tooth loss. It weakens gums and the tissues and bones that hold teeth in place. That makes it easier to get an infection, too.
One of the most surprising things about type 2 diabetes is that you can avoid it. To lower your risk, follow the same guidelines for warding off heart disease:
• Eat a healthy diet.
• Exercise for 30 minutes, 5 days a week.
• Stay at a healthy weight.
• Talk to your doctor about being tested for pre-diabetes.
People with pre-diabetes can avoid getting diabetes with lifestyle changes and medication. Below are the lifestyles that help prevent type 2 diabetes;
* Your Diet Makes a Difference
You can control blood sugar levels by changing your diet and losing extra weight. That will also cut your risk of complications. Carefully track the carbs in your diet. Keep amounts the same at every meal, watch how much fat and protein you eat, and cut calories. Ask your doctor to refer you to a dietitian to help you make healthy choices and an eating plan.
* Exercise Is Important
Regular exercise, like strength training or walking, improves your body's use of insulin and can lower blood sugar levels. Being active also helps get rid of body fat, lower blood pressure, and protect you from heart disease. Try to get 30 minutes of moderate activity on most days of the week.
* Relaxation Is Key
Stress can boost your blood pressure and blood sugar. Some people don't do anything for it. Others turn to food to cope with it. Instead, practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or visualisation. Talking to a friend, family member, counsellor, or a religious leader could help. If you can't beat it, reach out to your doctor.



















No comments:
Post a Comment